When comparing cardiorespiratory fitness levels of individuals differing in body size, it is best to look at the relative VO2max values rather than the absolute VO2max values.
What is the VO2?
VO2 max, or maximal oxygen consumption, refers to the maximum amount of oxygen that an individual can utilize during intense or maximal exercise. This measurement is generally considered the best indicator of cardiovascular fitness and aerobic endurance.
What is submaximal and maximal testing?
The methods more commonly used are: maximal exercise tests; submaximal exercise tests; and non-exercise tests. Maximal tests are accurate, but require medical monitoring when testing workers at medical risk. Submaximal tests are less accurate, but are safer and faster than a maximal test.
How do you measure VO2 max?
The primary way VO2 max is measured (and the original way) is by hooking yourself up to a mask and a heart rate monitor while running on a treadmill or riding a bike. The mask is connected to a device that measures the volume of oxygen you inhale and the amount of air you exhale.
How do you compare fitness levels?
These six tests are often used to help determine fitness level.
- A flexibility test, such as the sit and reach.
- An endurance test, such as the Cooper test.
- An upper body strength test, such as the push-up test.
- A core strength test, such as the plank test.
- A target heart rate test.
- A body size calculation, such as weight.
Why is there a lag time in the rise in oxygen consumption at the onset of exercise?
It takes some time for the cardiac output, for the muscle blood flow to increase, and for the oxygen to diffuse into the skeletal muscle tissue. Alternatively, oxygen delivery might increase quite quickly, and the lag might be due to sluggishness in mitochondrial respiration.
Why does oxygen consumption rise during long workouts?
Training results in an increase in the efficiency of oxygen transport within the body. By lowering the resting heart rate (HR), and the HR at sub maximal loads, the heart pumps more blood with every heart beat. This, in addition to other physiological changes, increases the oxygen extraction capability.
Frequently Asked Questions
What is the relationship between oxygen uptake and exercise intensity?
The characteristics of oxygen uptake (VO2) kinetics differ with exercise intensity. When exercise is performed at a given work rate which is below lactate threshold (LT), VO2 increases exponentially to a steady-state level.
What causes VO2 to increase during exercise?
What mechanisms might contribute to this increase in VO2? Well, most of it is due to changes within the active muscles themselves. 80 and in some studies as much as 90 to 100% of the increase in VO2 during prolonged exercise at the whole-body level can be attributed to changes in the active muscles.
What happens to VO2max during exercise?
When exercise is performed at a given work rate which is below lactate threshold (LT), VO2 increases exponentially to a steady-state level.
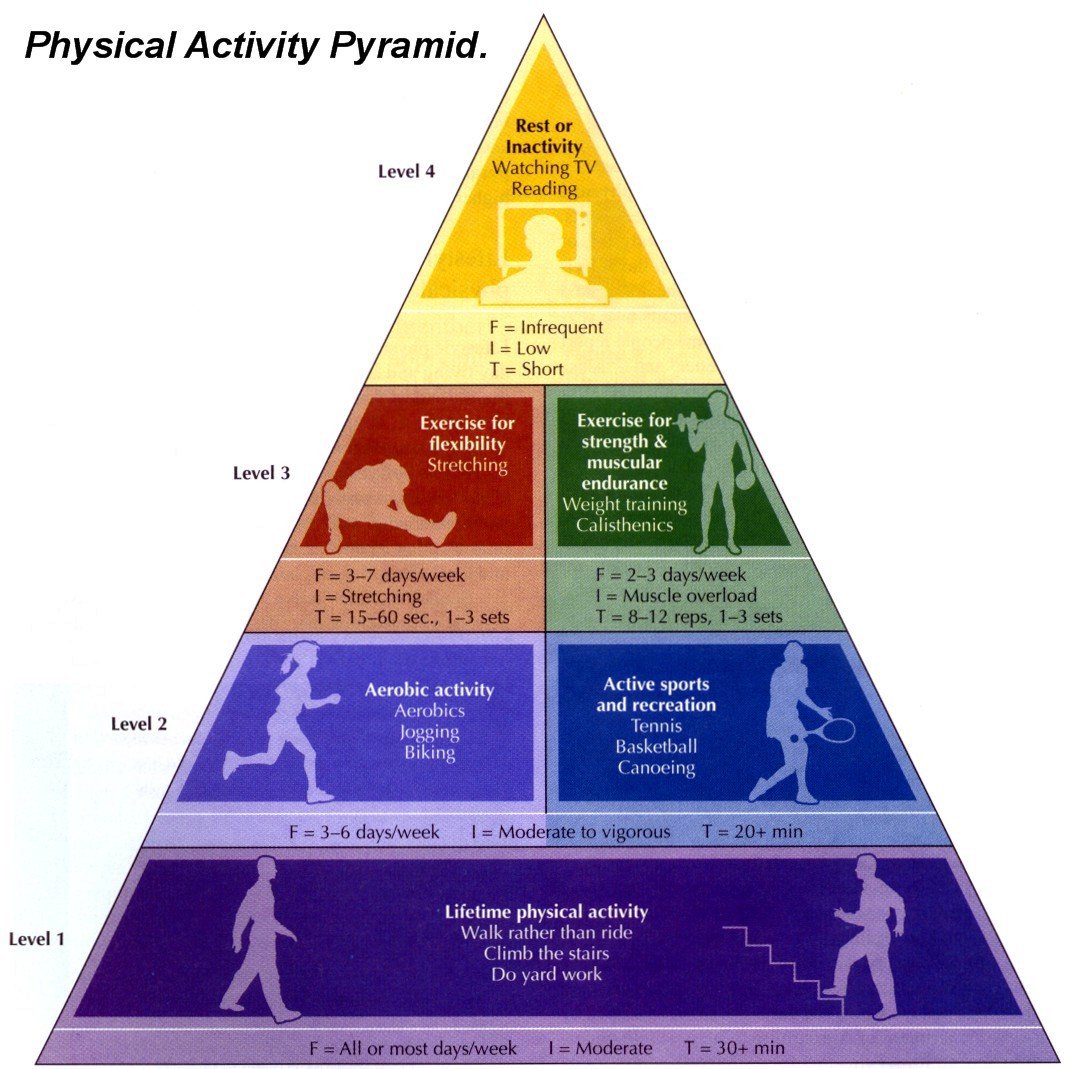
What are the 3 guidelines for aerobic exercise?
Aerobic Training Guidelines
- Frequency. Exercise aerobically 3 to 4 times a week.
- Intensity. Exercise hard enough to reach your target heart rate range.
- Time. Exercise aerobically for at least 20 minutes without stopping.
What are the 3 different intensity of aerobics?
As a rule of thumb:
- If you can talk and sing without puffing at all, you're exercising at a low level.
- If you can comfortably talk, but not sing, you're doing moderate intensity activity.
- If you can't say more than a few words without gasping for breath, you're exercising at a vigorous intensity.
FAQ
- What are the 3 levels of exercise intensity?
- Exercise is categorized into three different intensity levels. These levels include low, moderate, and vigorous and are measured by the metabolic equivalent of task (aka metabolic equivalent or METs). The effects of exercise are different at each intensity level (i.e. training effect).
- What are the three principles of exercise 3?
- These principles of training are Overload, Progression, and Specificity.
- What are some factors that account for variation in levels of fitness
- Jun 7, 2022 — Exercise needs vary between individuals for several reasons, the main one being that not everyone has the same fitness goals. For example, one
- What physiological factors make high intensity endurance exercise sustainable?
- By MJ Joyner · 2008 · Cited by 1505 — Elite athletic performance involves integration of muscular, cardiovascular and neurological factors that function cooperatively to efficiently transfer the
- What are the changes in cardiovascular variables during exercise?
- During exercise, increases in cardiac stroke volume and heart rate raise cardiac output, which coupled with a transient increase in systemic vascular resistance, elevate mean arterial blood pressure (60). However, long-term exercise can promote a net reduction in blood pressure at rest.
Which is used to compare fitness levels of individuals differing in body size?
| What does cardiovascular fitness increase? | Cardiovascular (aerobic) exercise: increases your energy and stamina • helps control blood pressure • improves your blood lipid profile (cholesterol) • helps you burn extra calories to maintain an ideal weight. Aerobic power helps an athlete sustain a challenging exercise pace over time. |
| How does cardiovascular endurance affect running? | If you have good cardiovascular endurance, you can exercise at medium intensity for a long time (and high intensity for a while) before it makes you tired. This is because your body is able to keep getting the oxygen it needs during exercise. |
| When exercising what causes an increase in cardiac output? | Cardiac output during exercise increases greatly owing to the relatively high heart rates that are achieved during exercise. Heart rate increases proportionately with workload until heart rates close to maximal are attained. |
| What are cardiovascular variables? | Cardiovascular variables such as heart rate, arterial blood pressure, stroke volume and the shape of electrocardiographic complexes all fluctuate on a beat to beat basis. These fluctuations have traditionally been ignored or, at best, treated as noise to be averaged out. |
| What does aerobic exercise increase muscle capillaries? | Exercising muscles need more blood. And in response to regular exercise, they actually grow more blood vessels by expanding the network of capillaries. In turn, muscle cells boost levels of the enzymes that allow them to use oxygen to generate energy. |
- Does aerobic training increase capillary density?
- There are two primary ways to do it. The first is through long slow distance (e.g., easy running or cycling). Research published in the Journal of Atherosclerosis and Thrombosis shows that several hour-long, low intensity cardio workouts per week can increase capillary density by more than 25 percent.
- How are capillaries affected by exercise?
- Exercise training increases the number of capillaries per square millimeter of muscle in humans and these increases are greatest in SO (Type I) and FOG (Type IIA) skeletal muscle (37–39).
- What happens when capillary density increases?
- An increase in capillaries results in an increase in blood flow to the muscles. An increase in blood flow provides muscles with increased supplies of oxygen and nutrients that give an increase in energy. When capillarisation is increased, muscles are able to work for longer periods of time without fatiguing.
- Does muscular endurance training increase capillaries?
- Thus, both endurance training and electrical stim- ulation induce an increase in the activity of oxidative enzymes which seems to precede the increase in capillary density related to individual muscle fibers.