Title: Why Does Stretching a Muscle Beyond Its Optimal Length Reduce Its Ability to Contract?
Meta Description: Discover the science behind why stretching a muscle beyond its optimal length can hinder its ability to contract effectively. Learn about the impact on muscle fibers and how it affects overall performance.
Introduction:
Stretching is an essential aspect of any fitness routine, helping to improve flexibility, prevent injuries, and enhance athletic performance. However, have you ever wondered why stretching a muscle beyond its optimal length can actually reduce its ability to contract effectively? In this article, we will delve into the science behind this phenomenon and understand the reasons behind it.
I. The Physiology of Muscle Contraction:
Before we explore why stretching a muscle beyond its optimal length affects its ability to contract, let's briefly understand the physiology of muscle contraction. Muscles are composed of individual muscle fibers, which are capable of contracting and generating force. These fibers consist of proteins called actin and myosin, which interact to produce the desired movement.
II. The Impact of Stretching Beyond Optimal Length:
When a muscle is stretched beyond its optimal length, several factors come into play that hinder its ability to contract effectively:
1. Disruption of Sarcomere Overlap:
- Sarcomeres are the basic functional units
What happens when a muscle is stretched beyond its optimal length?
If a sarcomere is stretched past the ideal length (beyond 120 percent), thick and thin filaments do not fully overlap, which results in less tension produced. If the muscle is stretched to the point where the thick and thin filaments do not overlap at all, no cross-bridges can be formed, and no tension is generated.
What happens when a muscle is stretched beyond its optimum length?
If the muscle is overstretched the tension will decrease. The actin and myosin filaments do not overlap causing a decrease in the number of cross-bridges that can form.
Why does stretching a skeletal muscle beyond resting length reduce the force of contraction?
If a sarcomere is stretched too far, there will be insufficient overlap of the myofilaments and the less force will be produced. If the muscle is over-contracted, the potential for further contraction is reduced, which in turn reduces the amount of force produced.
What happens when you stretch a muscle too far?
Overstretching can result in an injury, such as a strain or a sprain. To avoid overstretching or pushing your range of motion beyond your capability for flexibility take steps, such as: warming up properly before working out. using correct form during workouts and when stretching.
What results when a muscle is stretched beyond its normal range of motion?
A strain is when a muscle or tendon (tissue that attaches muscle to bone) is stretched too far. A strain is sometimes called a "pulled muscle." Depending on the level of muscle strain, it may heal within a few weeks, but reinjury can happen.
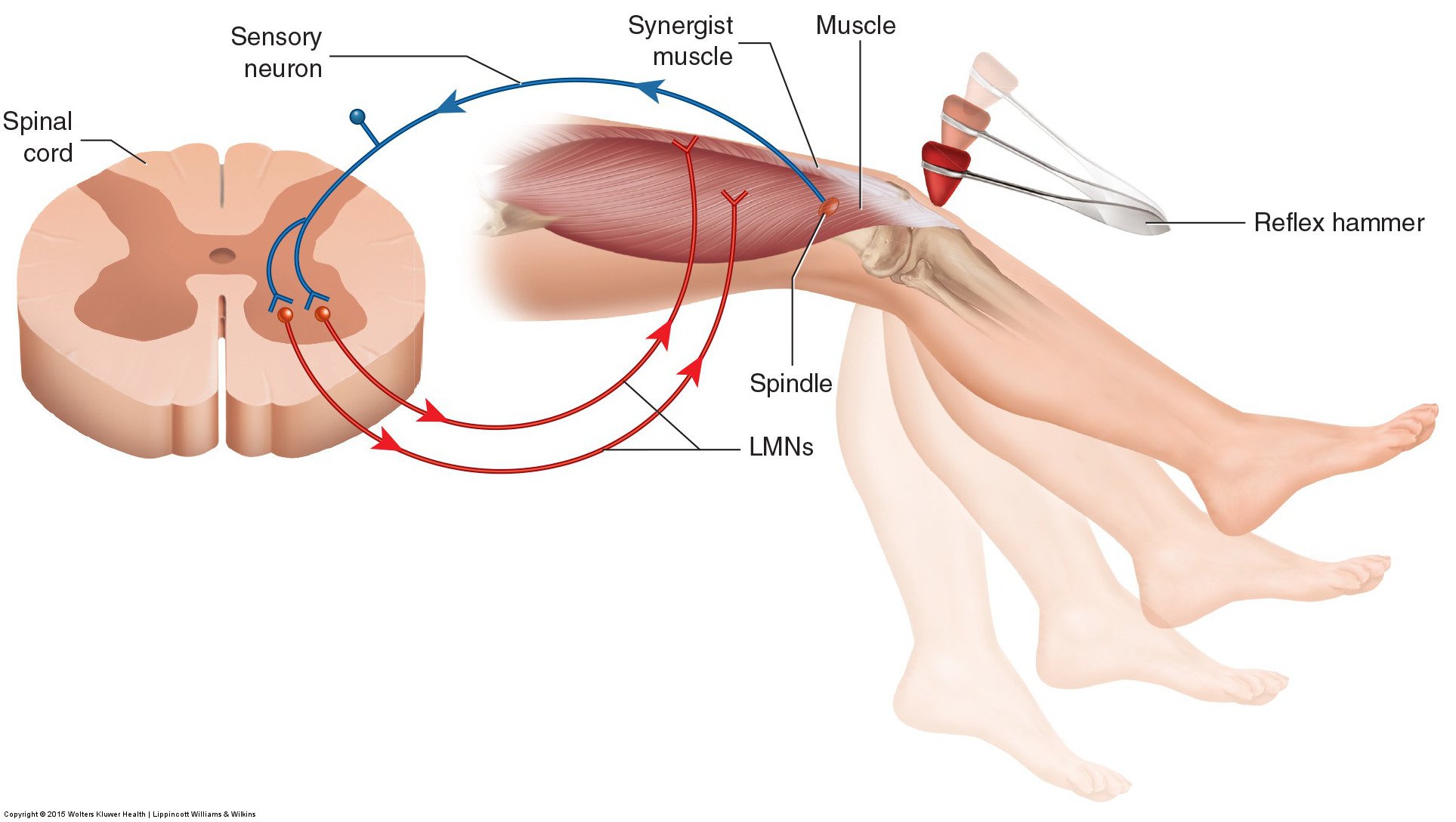
What is stretch detected by?
The muscle spindles in those muscles will detect this stretching, and the stretched muscles will contract to correct posture.
Frequently Asked Questions
What receptors detect stretching?
Muscle spindles are stretch receptors that signal the length and changes in length of muscles. They lie within an independent capsule, parallel to the main muscle. They are therefore stretched when the muscle lengthens but shorten when the muscle contracts.
Does stretching lengthen muscle fibers?
The stretching of a muscle fiber begins with the sarcomere, the basic unit of contraction in the muscle fiber. As the sarcomere contracts, the area of overlap between the thick and thin myofilaments increases. As it stretches, this area of overlap decreases, allowing the muscle fiber to elongate.
Can muscle fibers increase in length?
Muscle growth is determined by an increase in muscle fiber number (hyperplasia) as well as an increase in muscle fiber size (hypertrophy). The number of muscle fiber is determined before birth. Postnatal muscle growth mainly results from muscle hypertrophy through the increase in muscle fiber length and girth.
How long does it take to lengthen muscles?
With stretching, expect to spend eight weeks before seeing increased muscle length and joint movement.
Does stretching add sarcomeres?
Passive stretch may induce sarcomere addition if the muscle fibers are lengthened sufficiently to raise cytoplasmic calcium through stretch-activated calcium channels. The magnitude of stretch in vivo is limited by the physiologic range of movement and stretch pain tolerance.
FAQ
- What happens when a sarcomere is stretched?
- Stretching increases the amount of the already existent inhomogeneity of sarcomere lengths: weak, long sarcomeres will be stretched, and stronger sarcomeres will shorten7,8. Accordingly, the strong sarcomeres will have a filament overlap larger than the average sarcomere length, thus producing more force than expected.
- How does stretching affect muscle length?
- In terms of stretching, muscle tension is usually inversely related to length: decreased muscular tension is related to increased muscle length, while increased muscular tension is related to decreased muscle length.
- What increases sarcomere length?
- As sarcomere lengths increase, force is generated and increases to reach a maximum at sarcomere lengths of approximately 2.2 μm. At longer sarcomere lengths, there may even be a decrease in force.
- Does stretching change muscle length?
- More and more research shows that stretching does not make muscles permanently longer. Instead, stretching re-educates the nervous system to tolerate a greater degree of muscle extension without firing pain signals. It's simple: muscles are not short or long and cannot significantly change length without injury.
- What helps resist excessive stretching in skeletal muscle?
- Answer and Explanation: This protein is called titin. Titin binds the myosin proteins and keep them in the center of the protein, and when the muscle stretches, titin is able to stretch like elastin, and allow for tensile strength for the muscle as it is stretched outwards.
Why does stretching a muscle beyond its optimal length reduce its ability to contract
| What protein resists stretching? | The elasticity of titin molecules provides passive resistance to stretching of relaxed muscle. |
| Which muscle filament is responsible for resisting excessive stretching of muscle fibers? | Elastic fibers are important to muscle tissue since they resist excessive stretching and help muscle fibers spring back to its original length after being stretched. |
| What is excessive stretching of muscle fibers called? | A strain is when a muscle is stretched too much and part of it tears. It is also called a pulled muscle. A strain is a painful injury. It can be caused by an accident, overusing a muscle, or using a muscle in the wrong way. A muscle strain is the stretching or tearing of muscle fibers. |
| Which stretch receptor prevents overstretch of muscles? | The spindle is a stretch receptor with its own motor supply consisting of several intrafusal muscle fibres. The sensory endings of a primary (group Ia) afferent and a secondary (group II) afferent coil around the non-contractile central portions of the intrafusal fibres. |
| How does stretching affect connective tissue? | In ex vivo experiments, stretching of connective tissue reduced the migration of neutrophils and increased tissue RvD1 concentration. These results demonstrate a direct mechanical impact of stretching on inflammation-regulation mechanisms within connective tissue. |
- What does stretching do to the nervous system?
- Stretching decreases nerve stiffness. Peripheral nerves move and deform during stretching. Pain pressure thresholds increase following stretching.
- What are the effects of nerve stretching?
- Summary. We predict that the stretching of nerves will reduces their excitability in a manner reminiscent of the action of anesthetics. At constant stimulus, stretching will result in a decrease of the action potential amplitude due to its effect on the melting transition in membranes.
- What are the neurological changes in muscle to stretch?
- When a muscle lengthens, the muscle spindle is stretched and its nerve activity increases. This increases alpha motor neuron activity, causing the muscle fibers to contract and thus resist the stretching. A secondary set of neurons also causes the opposing muscle to relax.
- Is it important to stretch connective tissue?
- It was found that the connective tissue accumulation that occurs in inactive muscles can be prevented either by passive stretch or by active stimulation.
- Why does stretching a muscle beyond its optimal length reduce its ability to contract?
- Why does stretching a muscle beyond its optimal length reduce its ability to contract? Overstretching prevents myosin cross bridge interaction, since the